Glue dispensing equipment is a critical component in the manufacturing process of various products, ranging from electronics to automobiles to medical devices. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll provide an in-depth analysis of the different types of glue dispensing equipment, their applications, and the benefits they offer. By the end of this article, you’ll have a better understanding of how to choose the right equipment for your needs and maximize your efficiency and productivity.
Types of Glue Dispensing Equipment
There are three main types of glue dispensing equipment available in the market, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages:
Manual Applicators
Manual applicators are basic, handheld tools that allow operators to apply glue to products by squeezing a trigger or pressing a button. They are easy to use and affordable, but may not be suitable for high-volume production. Here are the working principles, advantages, and disadvantages of manual applicators:
Working Principle: Manual applicators work by using a flexible tube and a pinch mechanism to control the flow of adhesive through the system. The operator manually controls the flow of adhesive by squeezing the trigger or button, and the adhesive is applied to the desired area.
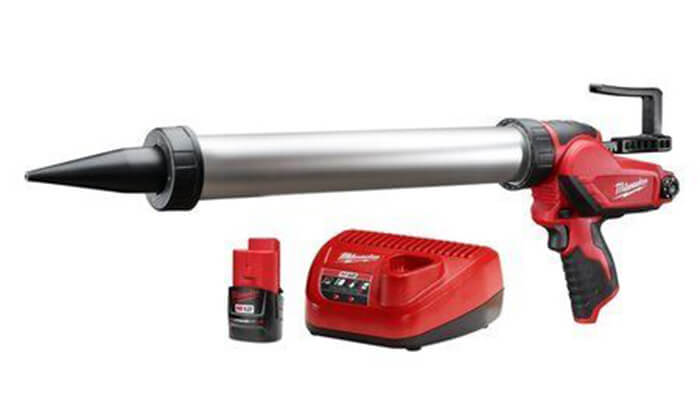

Advantages:
- Low cost and simple design
- Easy to use and portable
- Suitable for low- to medium-volume production
Disadvantages:
- Limited precision and control over flow rate and pattern
- Not suitable for high-volume production
- Can be tiring to use for long periods
Applications: Manual applicators are commonly used in industries such as construction, woodworking, and DIY projects where low-volume production and simple applications are required.
Metering Systems
Metering systems are more complex glue dispensing machines that use positive displacement pumps to accurately meter and apply adhesive. They are suitable for high-volume production and can handle a wide range of adhesive types and viscosities. Here are the working principles, advantages, and disadvantages of metering systems:
Working Principle: Metering systems use a positive displacement pump to accurately measure and dispense the adhesive. The adhesive is drawn into a reservoir, and then a piston or gear mechanism applies pressure to the adhesive, forcing it through a metering valve and out of the dispensing tip. The flow rate is controlled by adjusting the stroke length or speed of the pump.
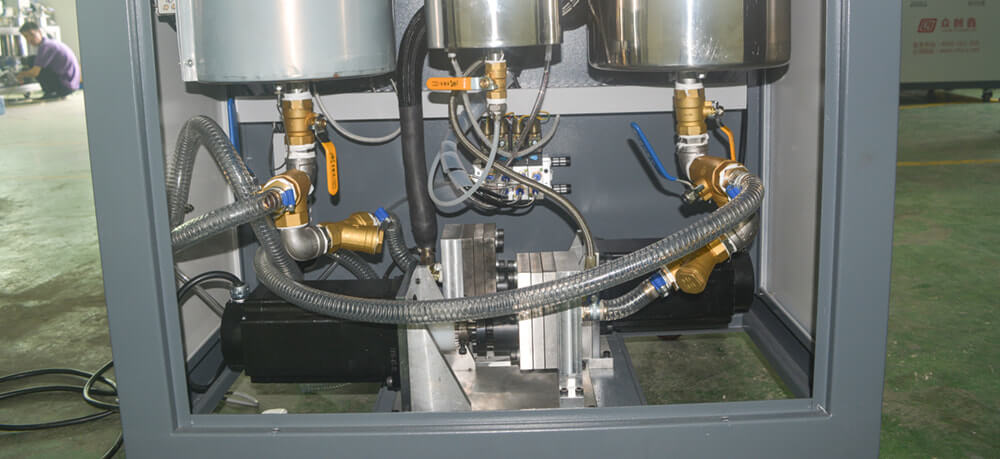

Advantages:
- Precise control over flow rate and pattern
- Suitable for high-volume production
- Can handle a wide range of adhesive types and viscosities
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost and complexity than manual applicators
- May require regular maintenance and calibration
- Limited mobility and portability
Applications: Metering systems are commonly used in industries such as automotive, electronics, and aerospace where high-volume production and precise control over adhesive flow rate and pattern are required.
Robots
Robots are the most advanced glue dispensing machines, which use automated arms and nozzles to apply adhesive with precision and consistency. They are ideal for high-volume production and can handle complex geometries and patterns. Here are the working principles, advantages, and disadvantages of robots:
Working Principle: Robots use automated arms and nozzles to dispense adhesive with precision and consistency. The system is programmed to apply the adhesive according to the desired pattern and flow rate, and the robot arm moves to the required location and applies the adhesive.
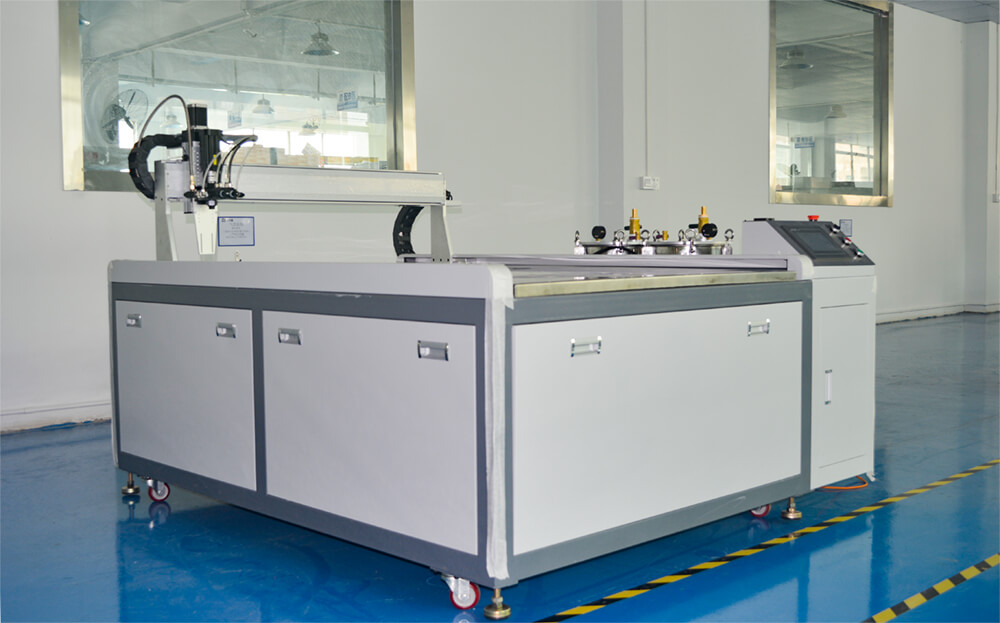

Advantages:
- High precision and repeatability
- Can handle complex geometries and patterns
- Can significantly increase productivity and efficiency
Disadvantages:
- High cost and complexity
- May require specialized training to operate and maintain
- Limited mobility and flexibility
Applications: Robots are commonly used in industries such as automotive, electronics, and medical devices, where high-volume production and precise control over adhesive application are required.
Process of Glue Dispensing Equipment
Glue dispensing equipment is used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, electronics, and medical devices. It is commonly used for applications such as:
- Bonding: Bonding is the process of using adhesive to join two or more parts together. The adhesive is applied to the surface of the parts, and then the parts are pressed together until the adhesive dries or cures. Bonding is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction to join materials such as metal, plastic, and composite materials. Bonding offers several advantages over other methods of joining, including improved strength and durability, reduced weight, and increased design flexibility.
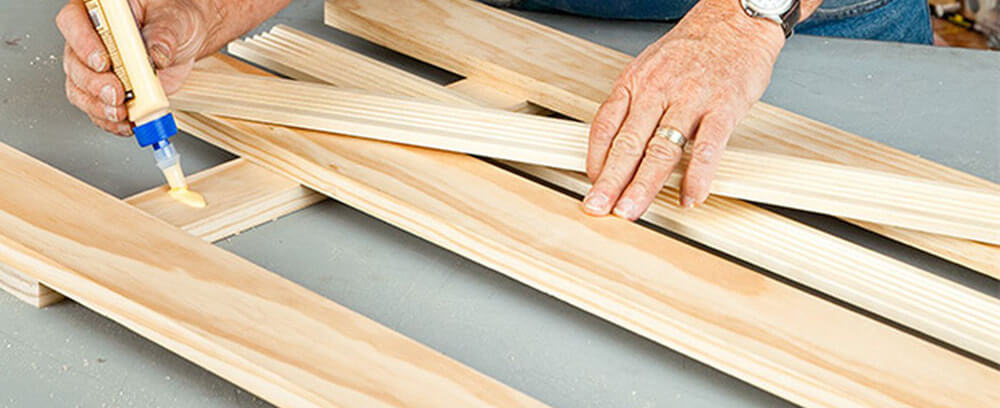

- Coating: Coating is the process of applying a thin layer of adhesive to the surface of a product to improve its performance or appearance. The adhesive is applied using a spray gun or other dispensing equipment, and then it is allowed to dry or cure. Coating is commonly used in industries such as electronics, automotive, and consumer products to protect the surface from damage, improve adhesion, or enhance the appearance of the product.
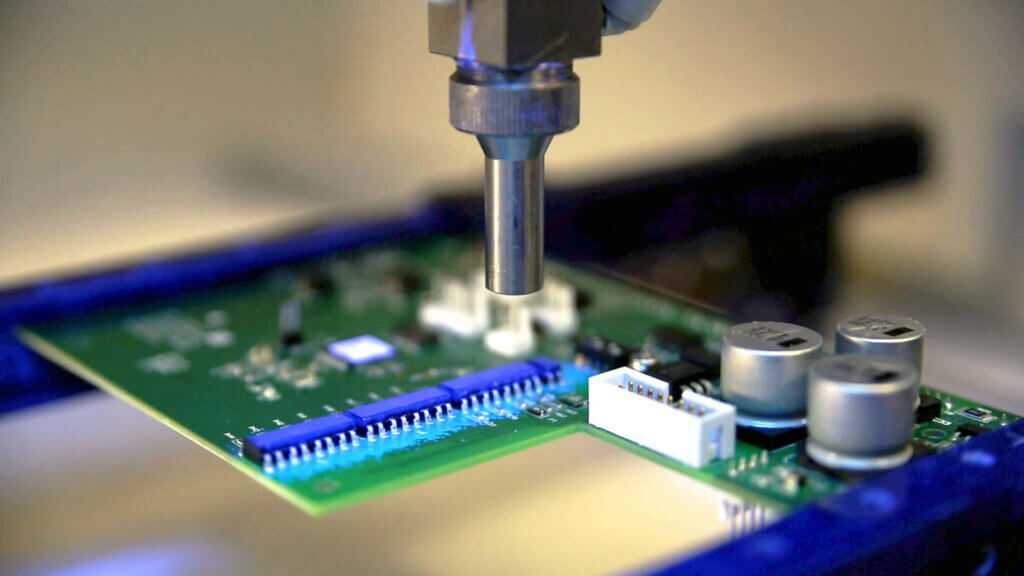
- Sealing: Sealing is the process of using adhesive to fill gaps or cracks in a product to prevent the leakage of fluids or gases. The adhesive is applied to the surface of the product, and then it is allowed to dry or cure. Sealing is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics to seal joints, seams, and other areas where leakage may occur. Sealing offers several advantages over other methods of sealing, including improved strength, durability, and chemical resistance.
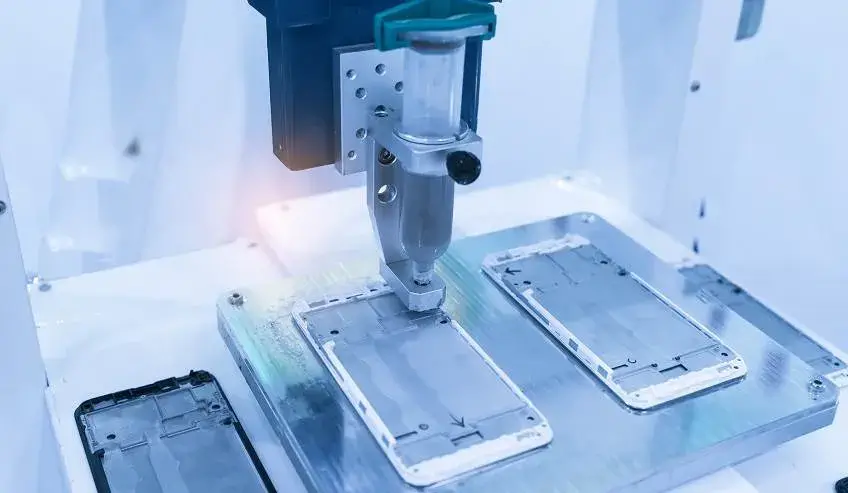

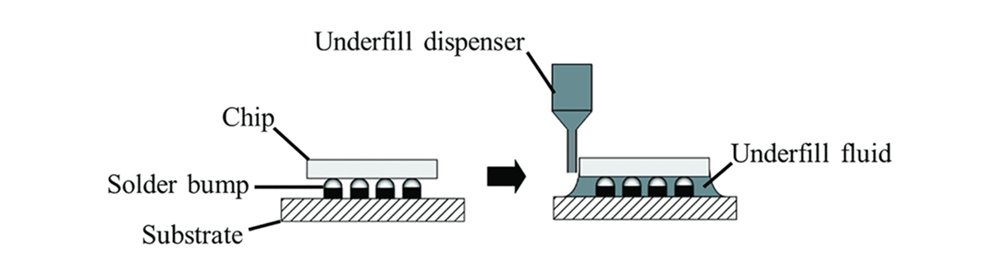
- Potting: Potting is the process of completely encapsulating a product or component in adhesive to protect it from external factors such as moisture, dust, and vibration. The adhesive is poured or injected into a container or mold that surrounds the product or component, and then it is allowed to dry or cure. Potting is commonly used in industries such as electronics, medical devices, and aerospace to protect sensitive components from harsh environments. Potting offers several advantages over other methods of encapsulation, including improved protection, reduced weight, and increased design flexibility.

- Encapsulating: Encapsulating is the process of using adhesive to completely encapsulate a product or component to protect it from external factors such as moisture, dust, and vibration. The adhesive is applied using a dispensing equipment, and then it is allowed to dry or cure. Encapsulating is commonly used in industries such as electronics, medical devices, and aerospace to protect sensitive components from harsh environments. Encapsulating offers several advantages over other methods of encapsulation, including improved protection, reduced weight, and increased design flexibility.
Selection Criteria for Glue Dispensing Equipment
The right equipment can ensure optimal performance, increase productivity, and reduce waste. However, selecting the right glue dispensing equipment can be a challenging task, as it involves considering several factors such as adhesive type, viscosity, and application requirements.
1. The type of adhesive used in the manufacturing process is an essential factor to consider when selecting glue dispensing equipment. Different adhesives have varying properties, such as viscosity, curing time, and chemical composition. Some common types of adhesives include:
- Cyanoacrylate: Fast-curing adhesive used for bonding metals, plastics, and rubbers.
- Epoxy: Two-part adhesive used for bonding metals, ceramics, and composites.
- Acrylic: Fast-curing adhesive used for bonding plastics and metals.
- Silicone: Flexible adhesive used for sealing and bonding in high-temperature applications.
2. Viscosity: The viscosity of the adhesive is a critical factor to consider when selecting glue dispensing equipment. The viscosity of an adhesive refers to its thickness or resistance to flow. It is measured in centipoise (cps). The selection of the appropriate pump depends on the adhesive viscosity and the required flow rate. Some common types of viscosity ranges for adhesives include:
- Low viscosity (less than 100 cps): Suitable for manual applicators or low-pressure dispensing systems.
- Medium viscosity (100 to 1,000 cps): Suitable for gear pumps or peristaltic pumps.
- High viscosity (more than 1,000 cps): Suitable for piston pumps or screw pumps.
3. Application Requirements: The application requirements of the product are another critical factor to consider when selecting glue dispensing equipment. Factors such as the desired flow rate, pattern, and precision of the application must be considered to ensure optimal performance. Different types of equipment, such as manual applicators, metering systems, and robots, offer varying levels of precision and control.
4. Material Compatibility: Material compatibility is another crucial factor to consider when selecting glue dispensing equipment. The equipment must be compatible with the materials used in the manufacturing process to ensure optimal performance and prevent damage to the product. The equipment must also be resistant to the chemicals in the adhesive. It is important to select equipment made from materials such as stainless steel or PTFE, which are resistant to most chemicals.
5. Maintenance and Service: Maintenance and service are essential factors to consider when selecting glue dispensing equipment. The equipment must be easy to maintain and service to ensure optimal performance and minimize downtime. It is important to select equipment from reliable manufacturers who offer excellent customer support and maintenance services.
Conclusion
Selecting the right glue dispensing equipment is a critical decision that can significantly impact the manufacturing process’s efficiency and quality. By considering the factors outlined in this article, such as adhesive type, viscosity, application requirements, material compatibility, and maintenance and service, you can ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Investing in high-quality glue dispensing equipment can lead to increased productivity, reduced waste, and improved product quality. Don’t compromise on the equipment’s quality, as it can impact the final product’s quality and cost. Trust reputable manufacturers who offer reliable equipment and excellent customer support to maximize the value of your investment.

